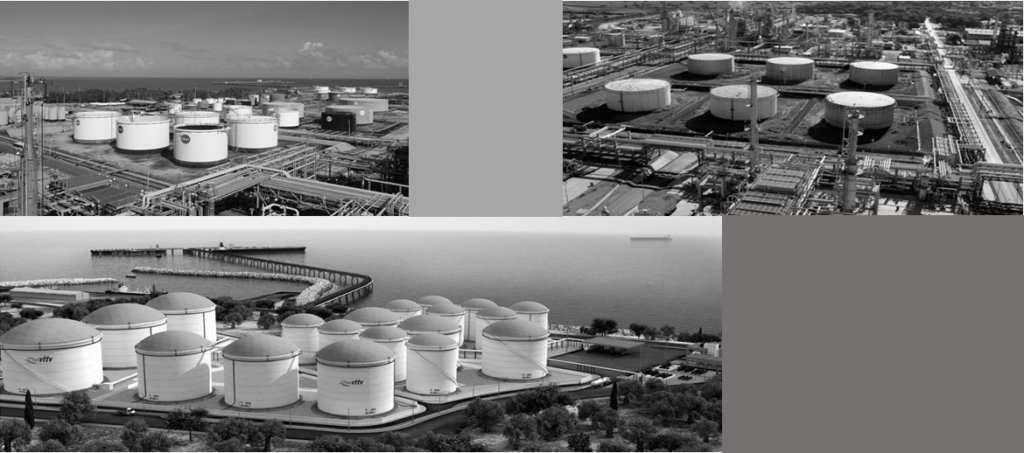
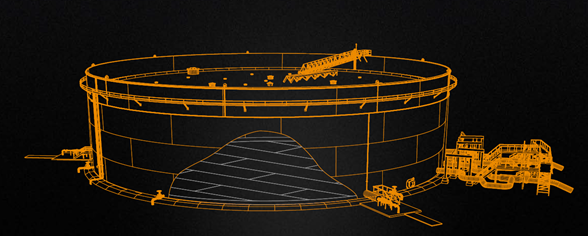
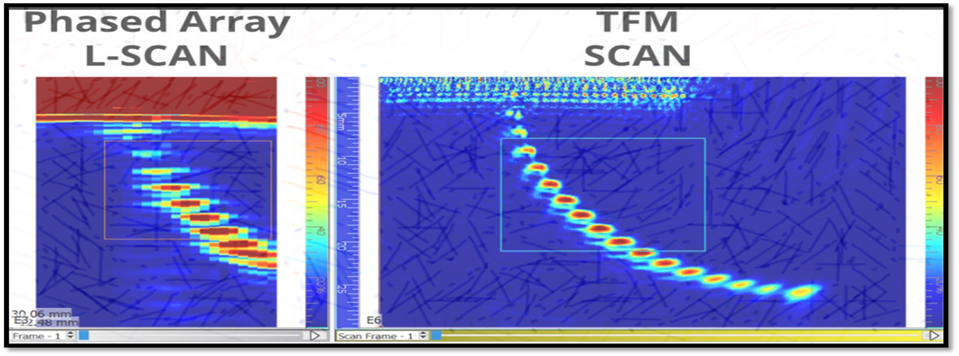
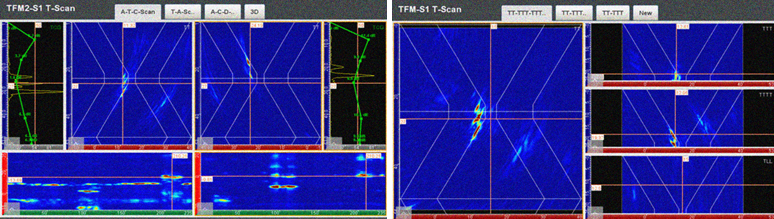
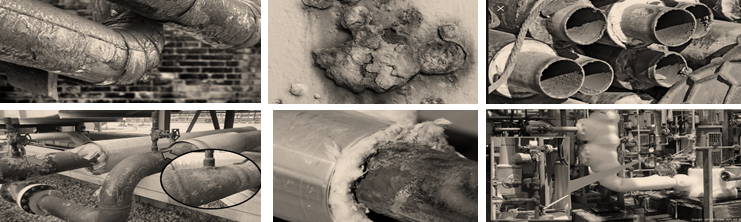
LNG Tanks are structures designed to store natural gas in a liquid state at atmospheric pressure. Depending on its chemical composition, the liquid state at atmospheric pressure is achieved by cooling the natural gas to a temperature below -160°C. Flat bottom cylindrical tanks can be from simple containment to full containment tanks. The outermost is usually a concrete cylinder with a framework of cryogenic bars and pre-stressed with circular and vertical steel cables. The full containment tanks are typically made up of 4 containers.